A few words
About Us
History
Our Journey: Decades of Dedication to Africa's Environment
Air Pollution
Rapid urbanization and industrialization have led to a significant increase in air pollution across many African cities.
Major sources include vehicle emissions, industrial activities, open waste burning, and the use of solid fuels for cooking and heating.
Poor air quality has been linked to rising rates of respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and premature deaths.
Tackling air pollution requires a multi-pronged approach involving stricter emissions standards, improved public transportation, and the promotion of clean energy alternatives.
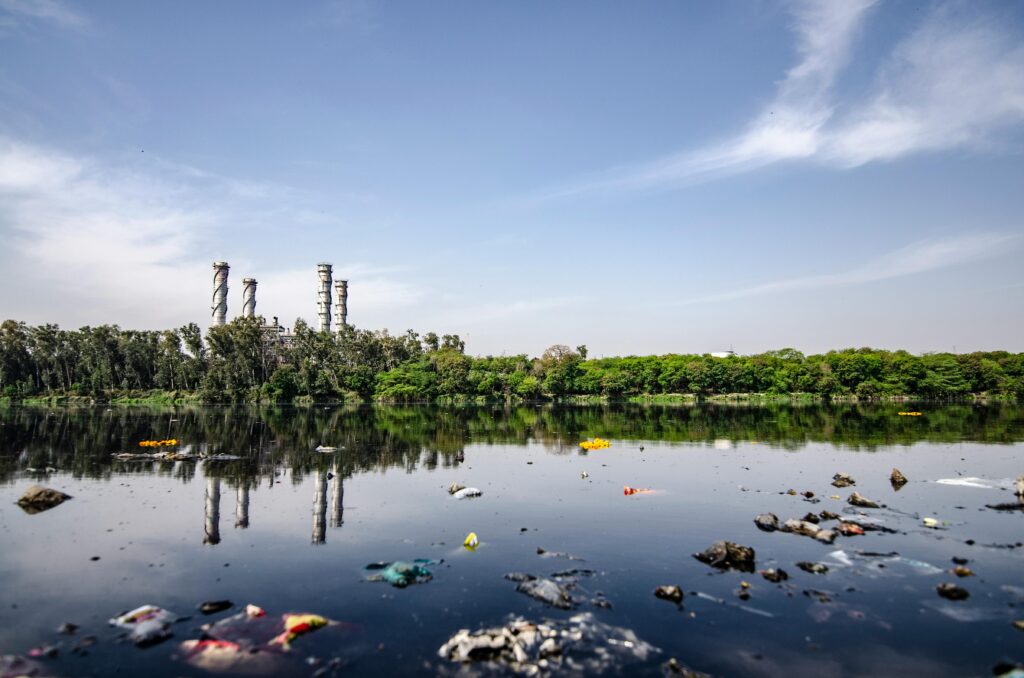
Water Pollution
Inadequate wastewater treatment, improper disposal of industrial effluents, and the use of pesticides/fertilizers have contaminated many of Africa’s water bodies.
Polluted water sources pose significant health risks, including the spread of waterborne diseases like cholera, dysentery, and typhoid.
Lack of access to clean drinking water and sanitation facilities disproportionately affects marginalized communities.
Integrated water resource management, enhanced treatment infrastructure, and public awareness campaigns are crucial to addressing water pollution.
Climate Change Impacts
Africa is particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, including rising temperatures, erratic rainfall patterns, and sea-level rise.
These changes threaten food and water security, increase the risk of extreme weather events, and exacerbate existing socioeconomic inequalities.
Vulnerable communities, such as smallholder farmers and coastal populations, are bearing the brunt of these impacts.
Adaptation strategies, such as drought-resistant agriculture, early warning systems, and coastal protection measures, are critical to building resilience.
Deforestation
Africa’s forests, which play a vital role in carbon sequestration and biodiversity conservation, are under threat from unsustainable logging, land clearing for agriculture, and urban expansion.
Deforestation not only contributes to climate change but also disrupts local ecosystems, displaces indigenous communities, and increases the risk of zoonotic disease outbreaks.
Promoting sustainable forest management, strengthening protected areas, and scaling up reforestation efforts can help reverse this trend.
Coastal Degradation
Coastal regions in Africa face a range of environmental challenges, including mangrove destruction, beach erosion, and marine pollution.
These issues threaten the livelihoods of coastal communities, who rely on fisheries and tourism, and undermine the natural defenses against storms and sea-level rise.
Integrated coastal zone management, habitat restoration, and sustainable tourism development are essential to safeguarding Africa’s valuable coastal environments.
Environmental Health Impacts
The interplay between environmental degradation and public health is a significant concern in Africa.
Issues like air pollution, water contamination, and exposure to hazardous chemicals can lead to a range of health problems, from respiratory diseases to neurological disorders.
Vulnerable populations, such as children and the elderly, are disproportionately affected by these environmental health risks.
Addressing the social determinants of health, strengthening environmental regulations, and promoting awareness are crucial to mitigating these impacts.
CLIMATE CHANG Effects in Africa .Climate change will increasingly impacts Africa due to many factors. These impacts are already being felt and will increase in magnitude if actions is not taken to reduce global Carbon emission . The impacts include higher temperatures, drought, changing rainfall pattern, and increase Climate Variability.
.CONSERVATION IN AFRICA AND PROTECTION OF ENDANGER SPECIES.
Come work with us
If you would like to work with an Environment Association with objective to bring change to the Natural Disasters Link to Deforestation and
Pollution our doors are open .